Cas9 nucleases can be programmed with single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) to mediate gene editing High CRISPR/Cas9mediated gene knockout efficiencies are essential for genetic screens and critically depend on the properties of the sgRNAs used The specificity of an sgRNA is defined by its targeting sequence Here, we discovered that two short sequence The seed segment of gRNA and PAM are two elements that determine Cpf1 specificity It seems that Cpf1 has a lower threshold for nonseed mismatches visavis Cas9 Seed region flanks at the initial part of the spacer and plays a notable role in the target specificity of CRISPR–Cpf1 system (FigGrna seed region Grna seed regionAn approach called CREATE enables multiplex genome engineering, protein engineering and mapping of mutations in bacterial and yeast cells Improvements in DNA synthesisDe Strasbourg à l'Est à NogentsurSeine à l'Ouest, la Région Grand Est s'étend sur 57 500 km² Elle compte 9 départements Ardennes, Aube

Type Ii Crispr Formulations Grnas Contain 4 Loop Structures Download Scientific Diagram
Grna seed region
Grna seed region-Importantly, the spacer region of the gRNA remains free to interact with target DNA Cas9 will only cleave a given locus if the gRNA spacer sequence shares sufficient homology with the target DNA Once the Cas9gRNA complex binds a putative DNA target, the seed sequence (810 bases at the 3′ end of the gRNA targeting sequence) will begin toThe guide RNA is a specific RNA sequence that recognizes the target DNA region of interest and directs the Cas nuclease there for editing The gRNA is made up of two parts crispr RNA (crRNA), a 17 nucleotide sequence complementary to the target DNA, and a tracr RNA, which serves as a binding scaffold for the Cas nuclease




Design And Synthesis Of Grna A Design Of Grna Dna Template Mix The Download Scientific Diagram
If gRNA expression is too high, reduction can be accomplished by inclusion of a UUU stretch in the seed region, which may lead to partial transcriptional termination and lower expression levels (Wu et al 14) Given the higher degree of specificity in plants, it is unlikely that gRNA expression levels are a general concern Since the seed region of gRNA is imperative for the activity, therefore, we calculated the GC content percentage of the PAM proximal seed region (1–12 nt) and the PAM distal region (13– nt) In the case of the PAM proximal seed region (1–12 nt), the GC content positively and significantly impacted the cleavage efficacy (pvalue = 32EThe presence of a single mismatch within the seed region of the guide sequence greatly reduced but did not abolish gRNA activity, whereas the presence of an additional mismatch, or the absence of a PAM, all but abolished gRNA activity Large insertions (≥ bp) of DNA vectorderived sequence were detected at frequencies up to 85% of total
After exposure to cas9/gRNA, we PCR out the region of interest for 1224 individual colonies and sequence through the cut site We then calculate the ratio of mutation or insertion/deletion at the cut site (indels) to unmodified wildtype sequence (wildtype) to get indel frequence = indels/wildtype*100 (as a percentage)GRNA sequence Genomic analysis results Seed region PAM AGG CGG AGG TCCTAAAC TCCTAAAC TCCTAAAC 1dentify target I loci where Cas9induced insertion or deletion (indel) formation will result in knockout of all isoforms of the gene, generally at 5´ exons 6 Filter out any overlapping sequences, if possible 7 Select the top 4 highestscoringFig 1 Focusing on the interaction between the seed region of gRNA and Cas9 protein (a) Interactive sites between the OH and the residues of Cas9 revealed by the crystal structure The numbering starts from the 50end of gRNA with a standard nt guide sequence (b) The guide sequence investigated for gene ASCL1 The seed region is
Tilapia miRNA125 was selected as the target to examine whether mutation could be induced in the seed region using CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA containing restriction enzyme Mse I was designed in the seed sequence of miRNA125 Coinjection of gRNA and Cas9 mRNA led to indels formation in the seed regionCheck the search result to identify gRNA spacer sequences that could be used to target selected gene or intergeneric region;This option allows users to calculate scores based on a particular region of the input sequences, such as the seed region of the gRNA Note that if the input sequence is longer than bp without PAM or 23 bp with PAM, only the first nucleotides are analyzed Results Page
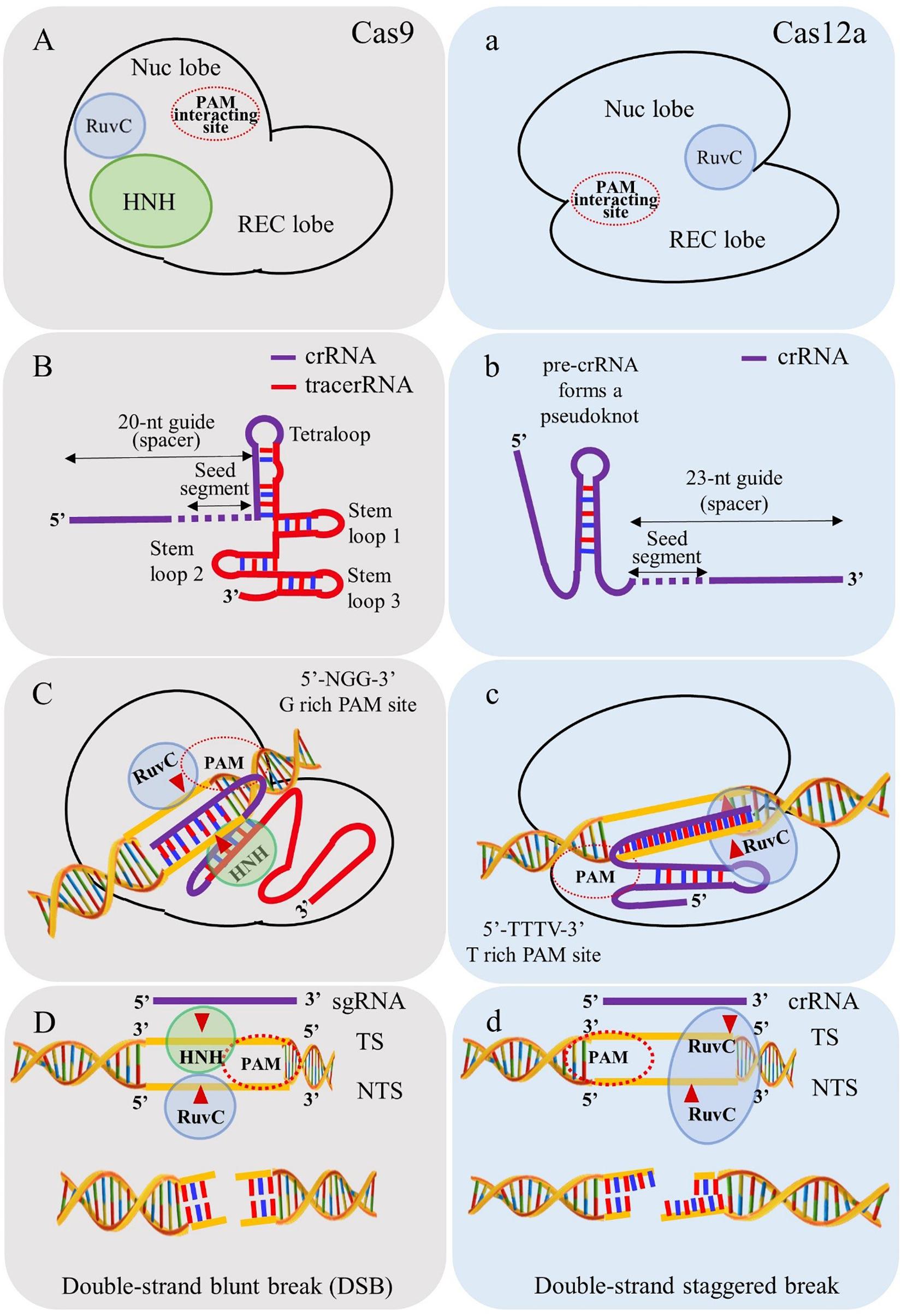



Frontiers Crispr Cas12a Cpf1 A Versatile Tool In The Plant Genome Editing Tool Box For Agricultural Advancement Plant Science
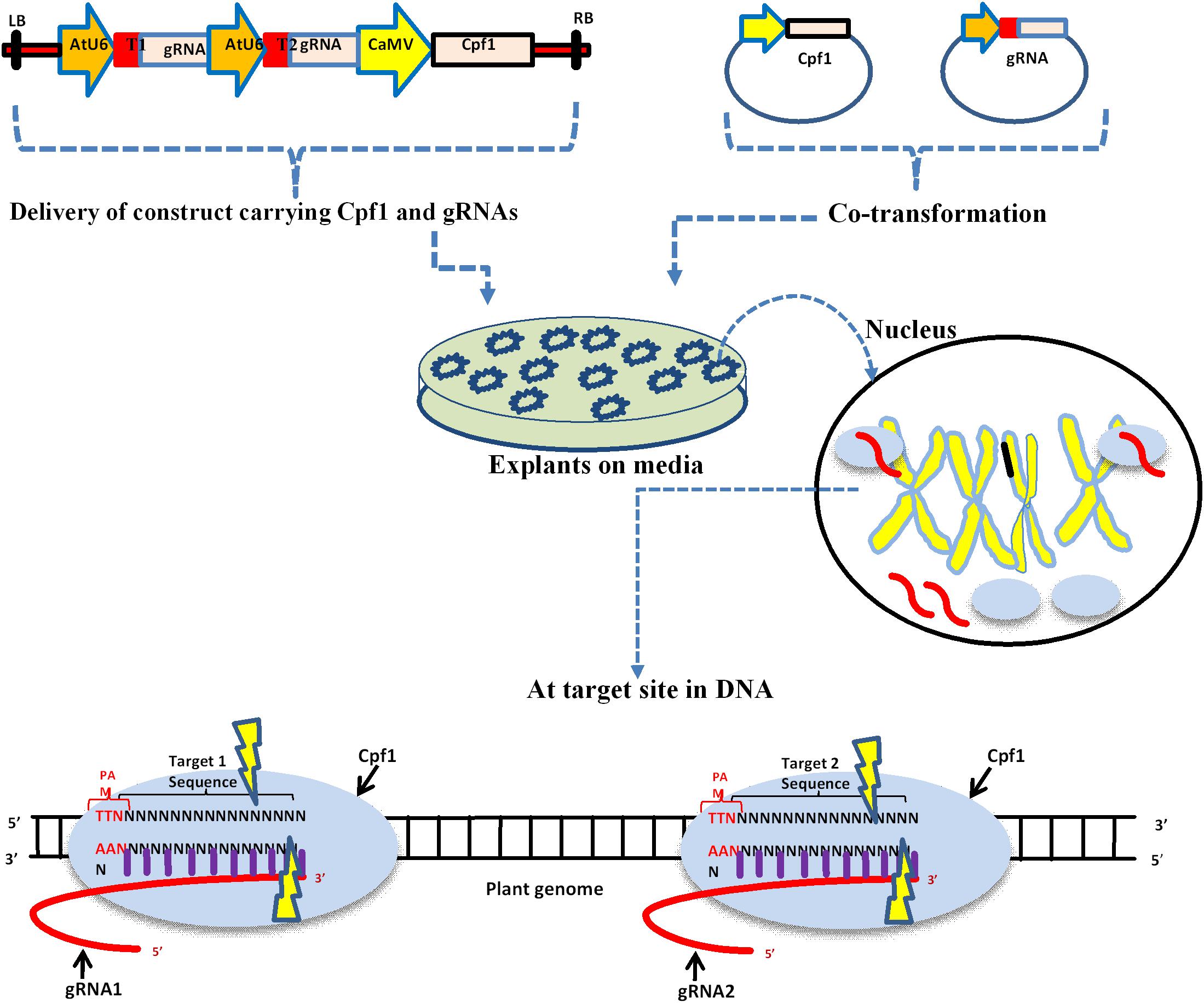



Frontiers The Rise Of The Crispr Cpf1 System For Efficient Genome Editing In Plants Plant Science
Truncating gRNA Length 16 Fu Y et al Improving CRISPRCas nuclease specificity using truncated guide RNAs Nat Biotech (14) gRNA sequences can be 17 nt in length to achieve similar levels of ontarget gene editing Up to 10,000 fold improvement in target specificity when truncated (17 or 18 base pair) gRNA is usedIn addition, we examined UUU in the gRNA seed region, which are the 6 nucleotides in the 5' PAMproximal region 41, and found that more inefficient gRNAs contains UUU in the seed region than efficient ones with an enrichment ratio of 029 (P = 907E02), which is consistent with previous CRISPRCas9 research 48Maximum number of mismatches in seed region tolerated by off targets Seed region stands for 6 nucleotides in the 5' PAMproximal region (Kim et al, 17) Relative to the target candidate sequence, sequences with more than this number of mismatches in the seed region will be excluded from consideration of offtarget effects
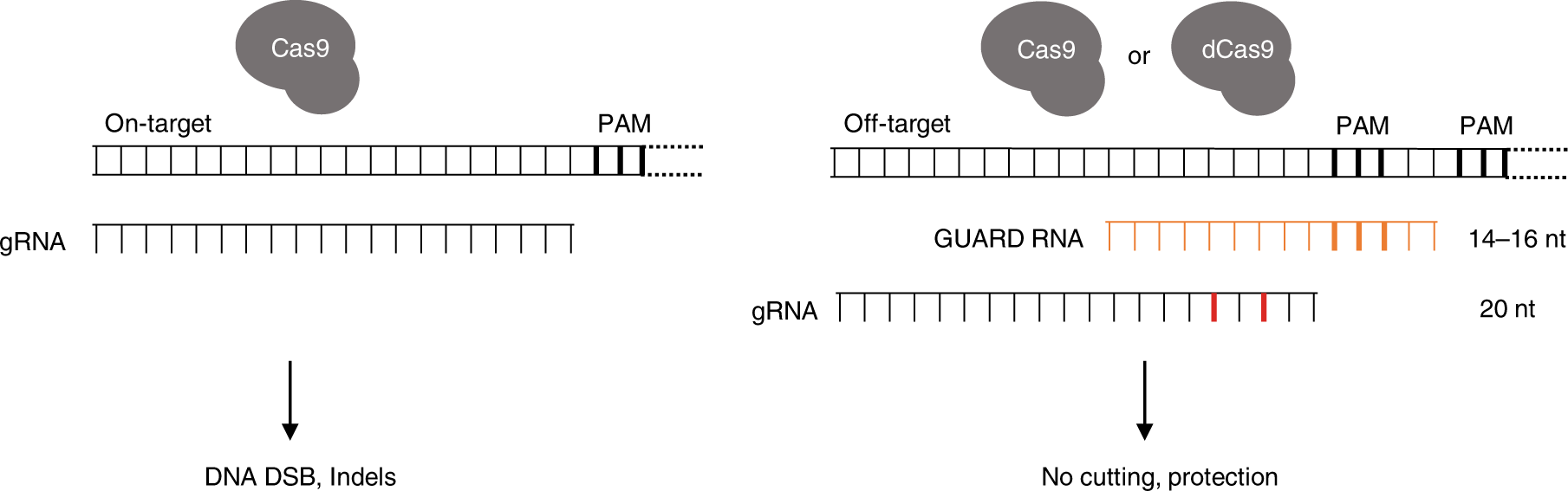



Crispr Guard Protects Off Target Sites From Cas9 Nuclease Activity Using Short Guide Rnas Nature Communications
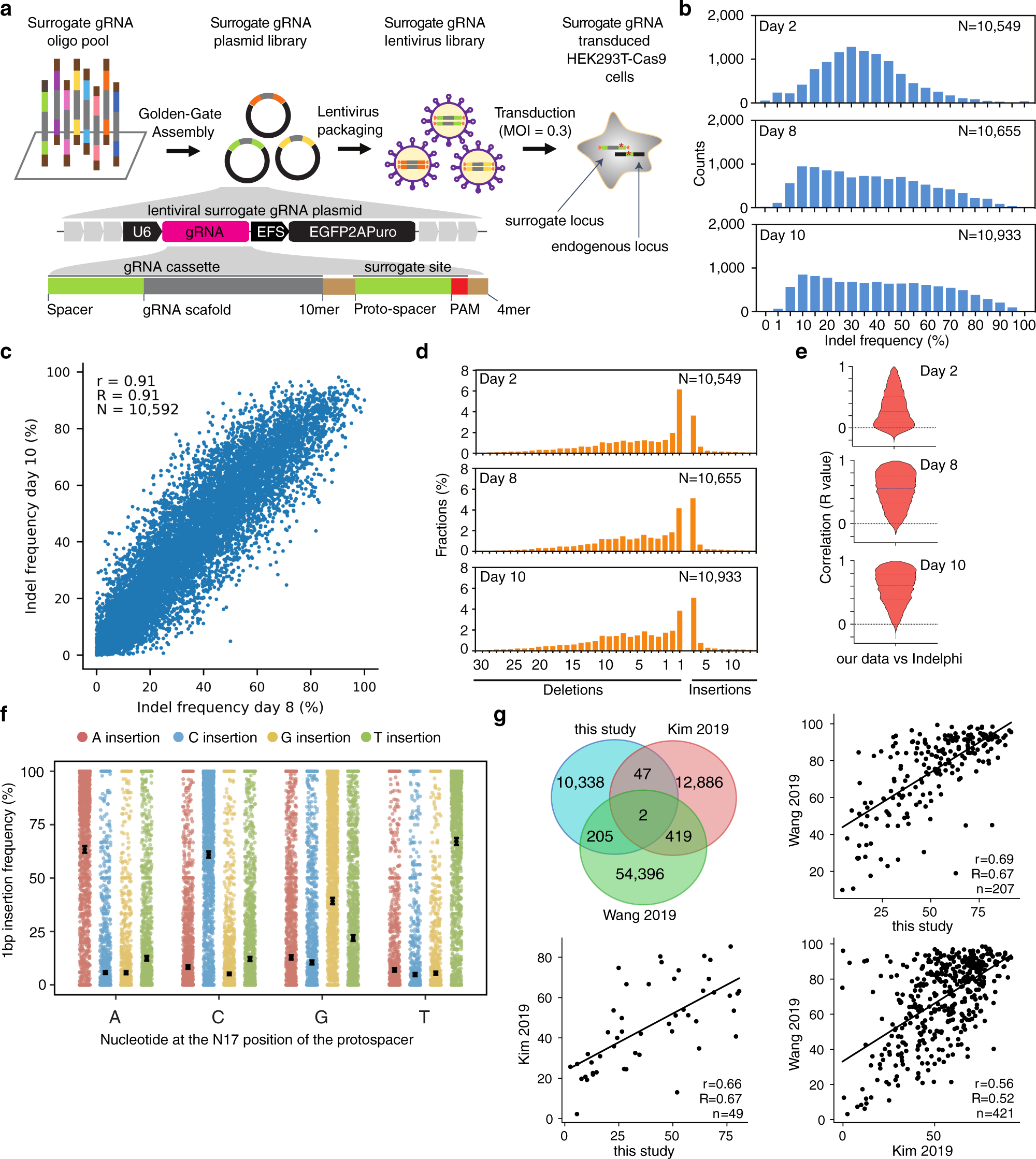



Enhancing Crispr Cas9 Grna Efficiency Prediction By Data Integration And Deep Learning Nature Communications
Seed and nonseed sequences were further segmented into three parts region I (1–7 bp), region II (8–12 bp) and region III (13– bp) As shown in Figure 3A, the seed region contains regions I and II, while the nonseed region only contains region III Investigation into SpCas9 specificity has revealed that both the 612 nt seed region of the gRNA recognition sequence and the adjacent PAM are important for nuclease activity 1314,17 Off target mutations can be minimized by ensuring that the seed region and adjacent PAM are unique in the genome being modified 14,16 If the seed region would bind to position 51–53 of the gRNA, it would be nonfunctional The findings from both of these publications can be correlated with the efficiency of the used gRNAs Comparing between the two DNA single strands, the nontranscribed DNA strand should be targeted by the gRNA for an enhanced efficiency 3




Addgene Crispr Guide



Profiling Single Guide Rna Specificity Reveals A Mismatch Sensitive Core Sequence Scientific Reports
The gRNA seed region is then able to hybridize smoothly with the apical loop of hairpin IV This positioning consolidates gRNAmRNA interactions such that the 5′phosphodiester bond of mRNAB) mismatches within the PAMproximal 8–12 nucleotide seed region of the guide sequence reduce gRNA activity to a greater degree than mismatches Each gRNA candidate was compared with all known exon sequences in the genome Recent experimental studies revealed that the 3′ end seed region of the gRNA is more relevant to offtargeting than the nucleotides residing in the 5′ end Thus, a more stringent filter is applied to this PAMproximal seed region
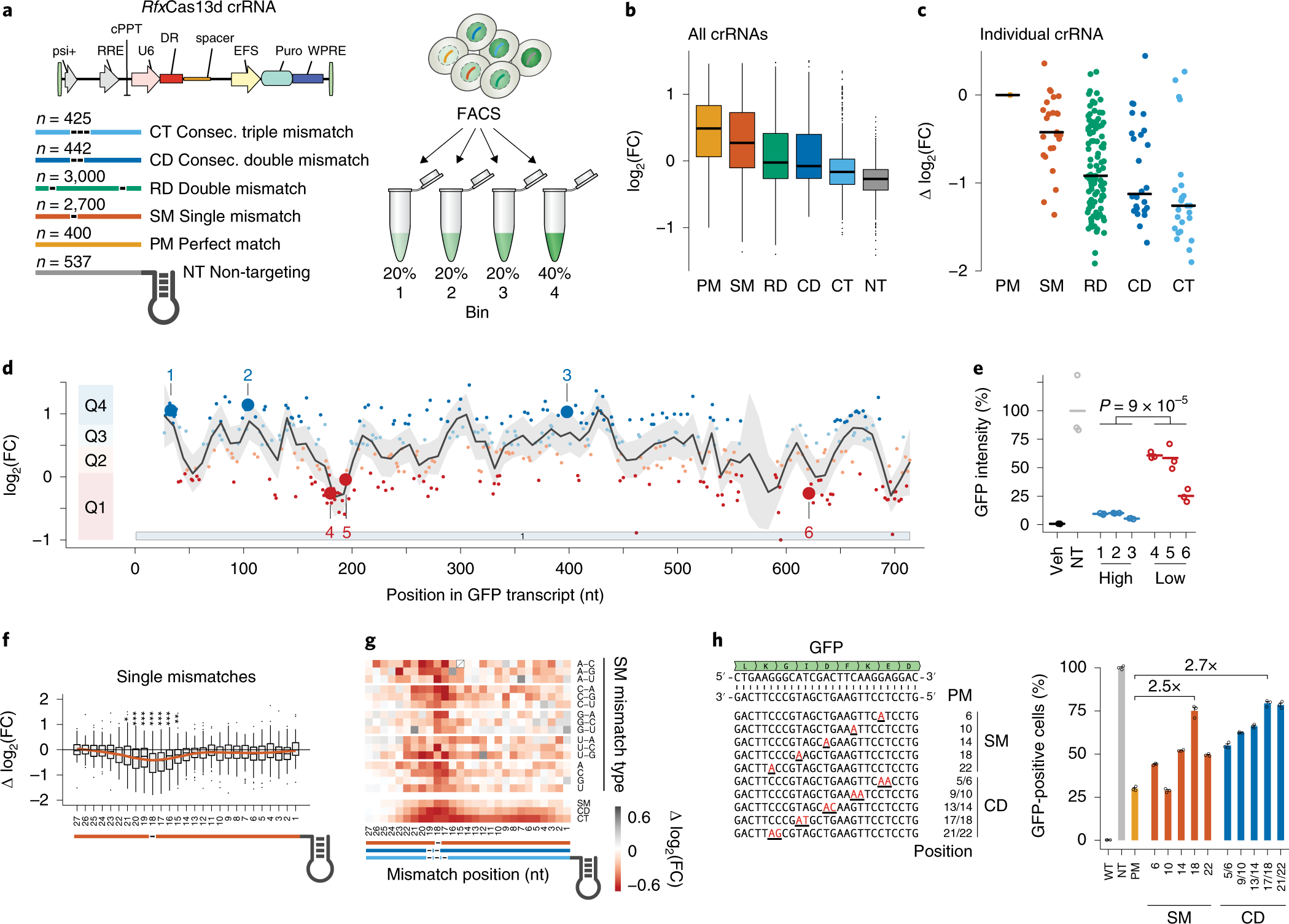



Massively Parallel Cas13 Screens Reveal Principles For Guide Rna Design Nature Biotechnology




High Throughput Assay For Nicking And Cleavage By Crispr Cas Download Scientific Diagram
GRNA seed region, and found that more inefficient gRNAs contain UUU in the seed region than efficient ones with an enrichment ratio of 008 ( P ¼ 286EAccompanies basepairing in the PAMdistal region, activating the endonuclease, and cutting both strands of DNA upstream of position 3 in the protospacer (7) One consequence of the zipping model is that the gRNAprotospacer duplex can be divided into two functional domains Basepairing within the seed, or PAMproximal region (positions 110),CasFinder Guide RNA design for the CRISPR/Cas9 system Genome Mp JGI 31 MpTak1 v51 Search conditions Length of gRNA 18 nt, Seed Region 9 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Length of gRNA nt, Seed Region 8 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Enter your sequence (s) in FASTA format below (Please make your sequence as short as possible!




Design And Synthesis Of Grna A Design Of Grna Dna Template Mix The Download Scientific Diagram




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram
The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary The PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a SacI site Subsequently, three gRNA–Cas9 constructs were made by inserting the synthetic DNA oligonucleotides which encode the gRNA seed into the pRG vectorCurrently, CRISPRPLANT will show all Class00 and Class10 gRNA spacer sequences We will add other gRNA spacer information in the near future Following information will be listed for each spacer sequence



1



Academic Oup Com
Recently, Wessels et al showed that the seed region (15–21 nucleotides) in gRNA is critical for CRISPR/Cas13d activity A single mismatch in the seed region led to diminished activity, and two or three mismatches led to severe reduction in Cas13d activity in this studyGuide RNA (gRNA) is a piece of RNAs that function as guides for RNA or DNAtargeting enzymes, which they form complexes with Very often these enzymes will delete, insert or otherwise alter the targeted RNA or DNA They occur naturally, serving important functions, but can also be designed to be used for targeted editing, such as with CRISPRCas9 The canonical seed region of all eAgos and some pAgos is composed of the second to eighth nts of the gRNA and has an Aform helical conformation in the Ago RNP complex (18 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ –23) Furthermore, the second to fourth bases of the seed sequence are exposed to the solvent for interaction with the complementary substrate ( 22 )




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect




Sample Input File And Possible Off Target Types In The Casot Download Scientific Diagram
Using reconstituted MpAgo RNPs with 5'BrdUmodified gRNAs, we mapped the seed region of the gRNA and identified the nucleotides of the gRNA that play the most significant role in targeting specificity We also show that these MpAgo RNPs can be programmed to distinguish between substrates that differ by a single nucleotide, using permutationsWong et al further analyzed the dataset of Doench et al and reported that nucleotides at position 18– are the seed region of the gRNA This region and the nucleotides located at 51–53 should be unbound and accessible to form efficient gRNAs If the seed region would bind to position 51–53 of the gRNA, it would be nonfunctional Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram Seed Market Size Share Growth Industry Research Report 23 Otherwise reject R (0) i (3) For each region, find all points that arecompatible with the region byGreat Lakes / New England;6/8/15 Further discussion Watershed method tries to grow regions




Modification Of Cas9 Grna And Pam Key To Further Regulate Genome Editing And Its Applications Sciencedirect




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect
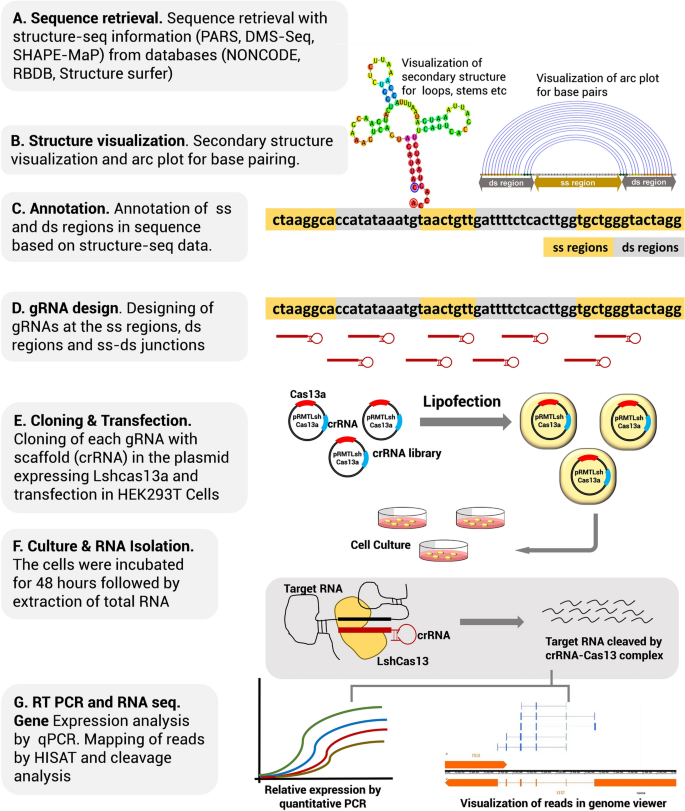
Once the PAM is recognized, the guide region of the gRNA undergoes seed nucleation to form an Aformlike helical RNADNA hybrid duplex Only once the RNA and DNA complete Rloop formation, also known as the zipped conformation, and structural rearrangement of the nuclease domains commence, can the endonuclease cut the DNA creating a DSB The PS1–gRNA seed region (22 nt) was predicted to pair with the template strand of OsMPK5, and would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a KpnI site The PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a SacI site Subsequently Binding of central seed region in gRNA crucial for Cas13 mediated cleavage (A) Schematic of central seed region of the guide in the crRNA binding the protospacer (target) region in the RNA (B) (Left) Schematic illustrating gRNAs targeting the SS and DS regions in the RNA structure The central segment (in Red) in the gRNA is the central seed
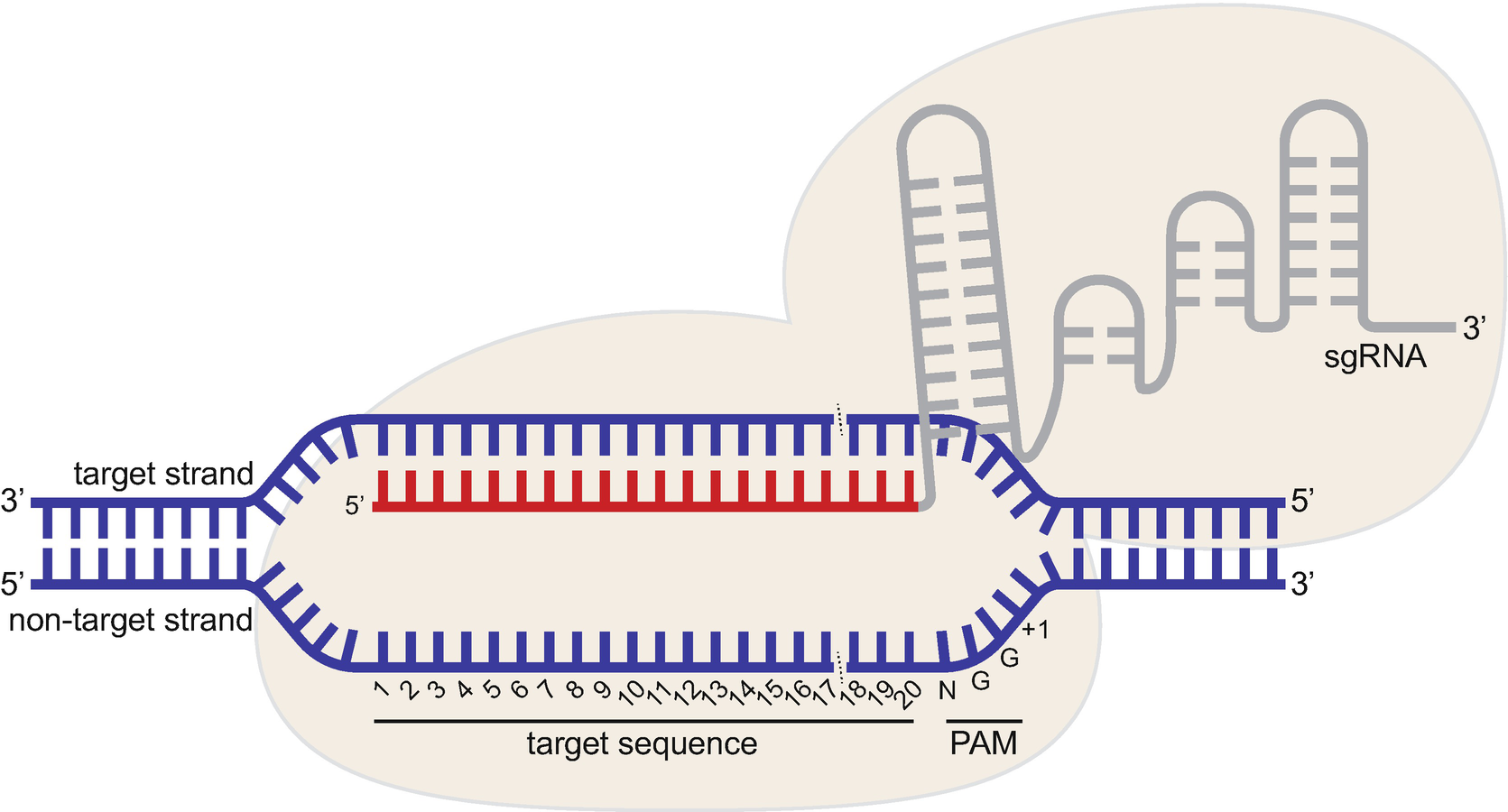



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Design Rules For Predicting Activity Springerlink




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of The Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Abstract Europe Pmc
The PS1–gRNA seed region (22 nt) was predicted to pair with the template strand of OsMPK5, and would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a KpnI site The PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a SacI site (Figure 2B Our results are consistent with established models of gRNA specificity 27,28,29,30 in which a) the absence of a canonical PAM site (5′NGG3′) greatly reduces or abolishes gRNA activity; The gRNA seed region is then able to hybridize smoothly with the apical loop of hairpin IV This positioning consolidates gRNAmRNA interactions such that the 5′phosphodiester bond of mRNA nt333 becomes the primary hydrolytic cleavage site Thereafter, nt14nt18 of the gRNA maps directly onto pseudoknot (I) that complements interior loop IIIf




Overview Of Guide Rna Design Tools For Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology




Programmable Rna Recognition Using A Crispr Associated Argonaute Pnas
The group then looked beyond the 'seed' region and used structural biology and mutational analysis to examine the effects of surrounding nucleotide context on knockdown efficiency, as well as the impact of gRNA folding and secondary structures Central seed binding region in gRNA crucial for transcript cleavage Our further motive was to evaluate the requirement of the singlestranded nucleotides in the target RNA necessary to complement It was suggested that the gRNA sequence of CRISPRCpf1 should be divided into seed (6 nt in the 5' PAMproximal end) and nonseed (14 nt in the 3' PAMdistal end) regions (Kim et al, 17b, 18) The tolerant ability of mismatches in the seed region is lower than that in the nonseed region
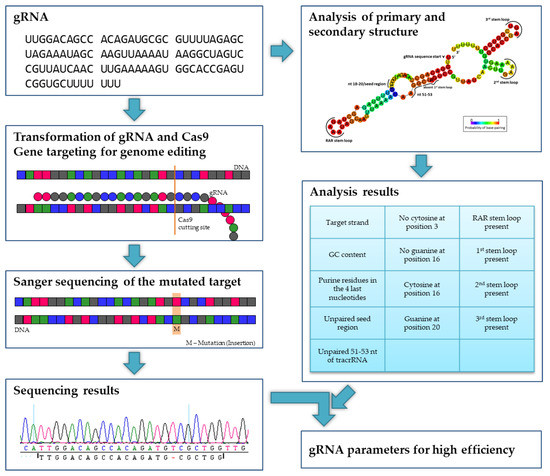



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html




Addgene Crispr Guide
The central segment (in Red) in the gRNA is the central seed region (Right) SS and DS stranded regions in the RNA structure are shown as arc plot, along with the targeting gRNAs gRNAs (a,



Sgrnacas9 A Software Package For Designing Crispr Sgrna And Evaluating Potential Off Target Cleavage Sites
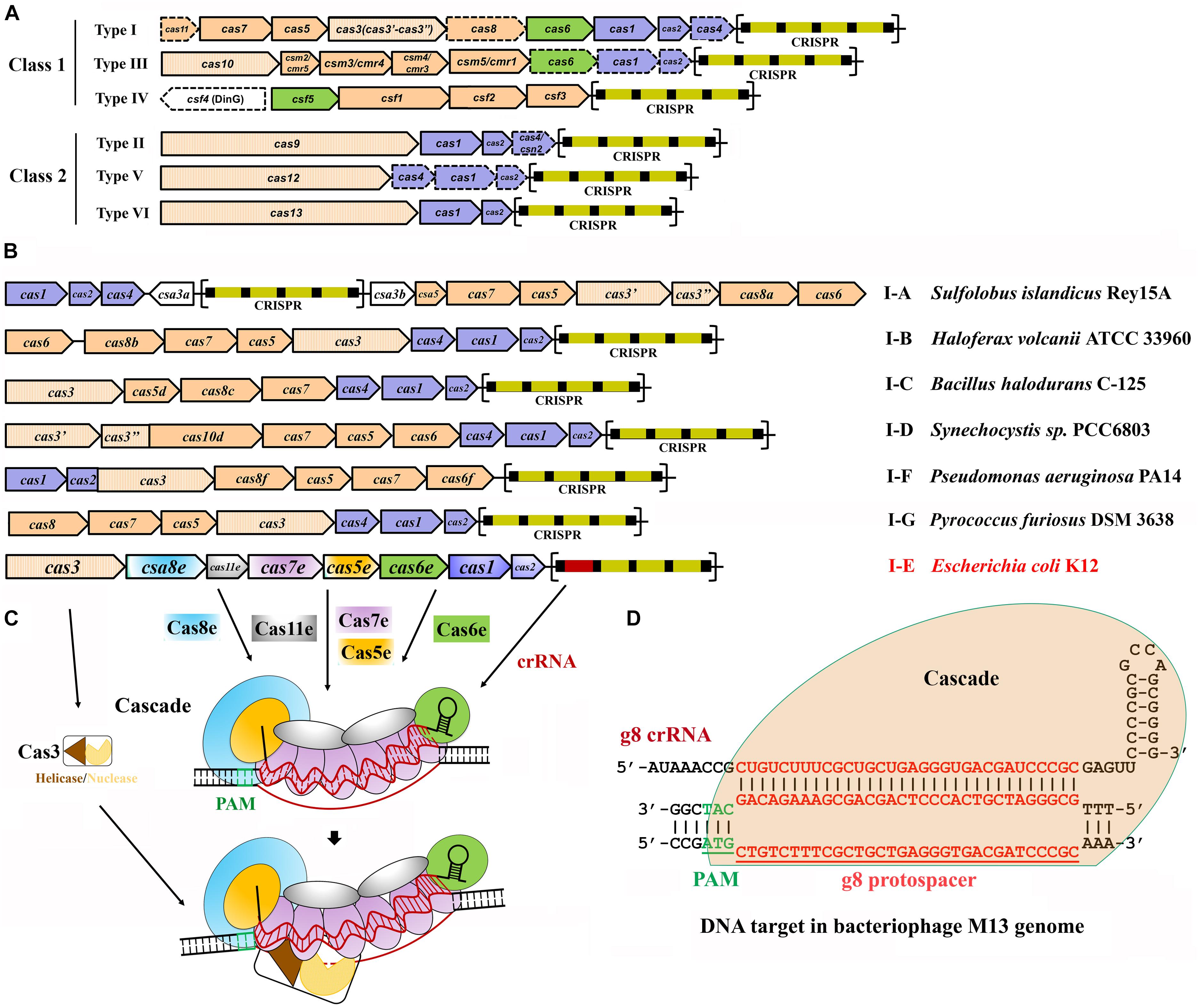



Frontiers Endogenous Type I Crispr Cas From Foreign Dna Defense To Prokaryotic Engineering Bioengineering And Biotechnology
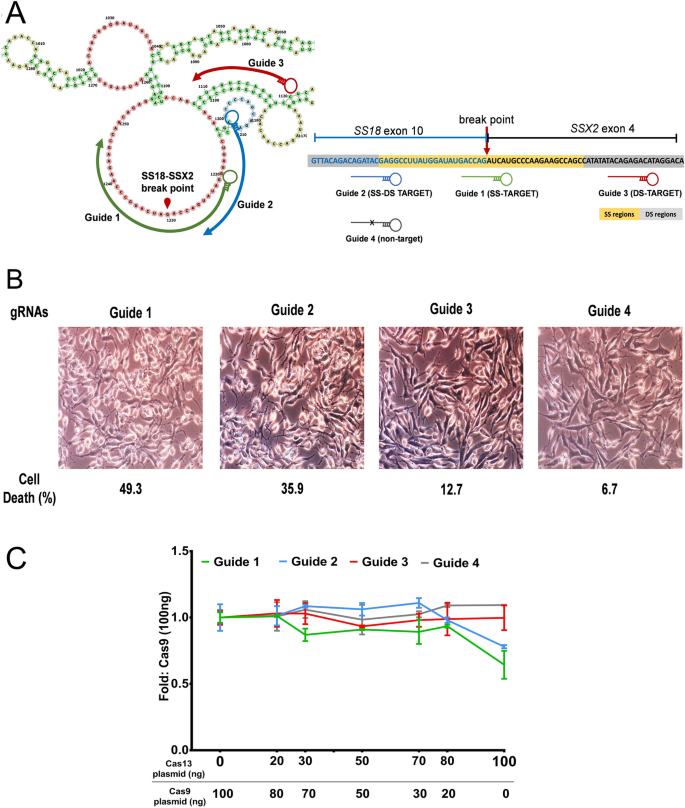



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports




The Crispr Cas9 System For Plant Genome Editing And Beyond Sciencedirect



Crispr Grna Guide Rna Design Tool For Eukaryotic Pathogens




Crispr Plant



Casot A Genome Wide Potential Cas9 Grna Off Target Searching Tool



Mdpi Com




Type Ii Crispr Formulations Grnas Contain 4 Loop Structures Download Scientific Diagram
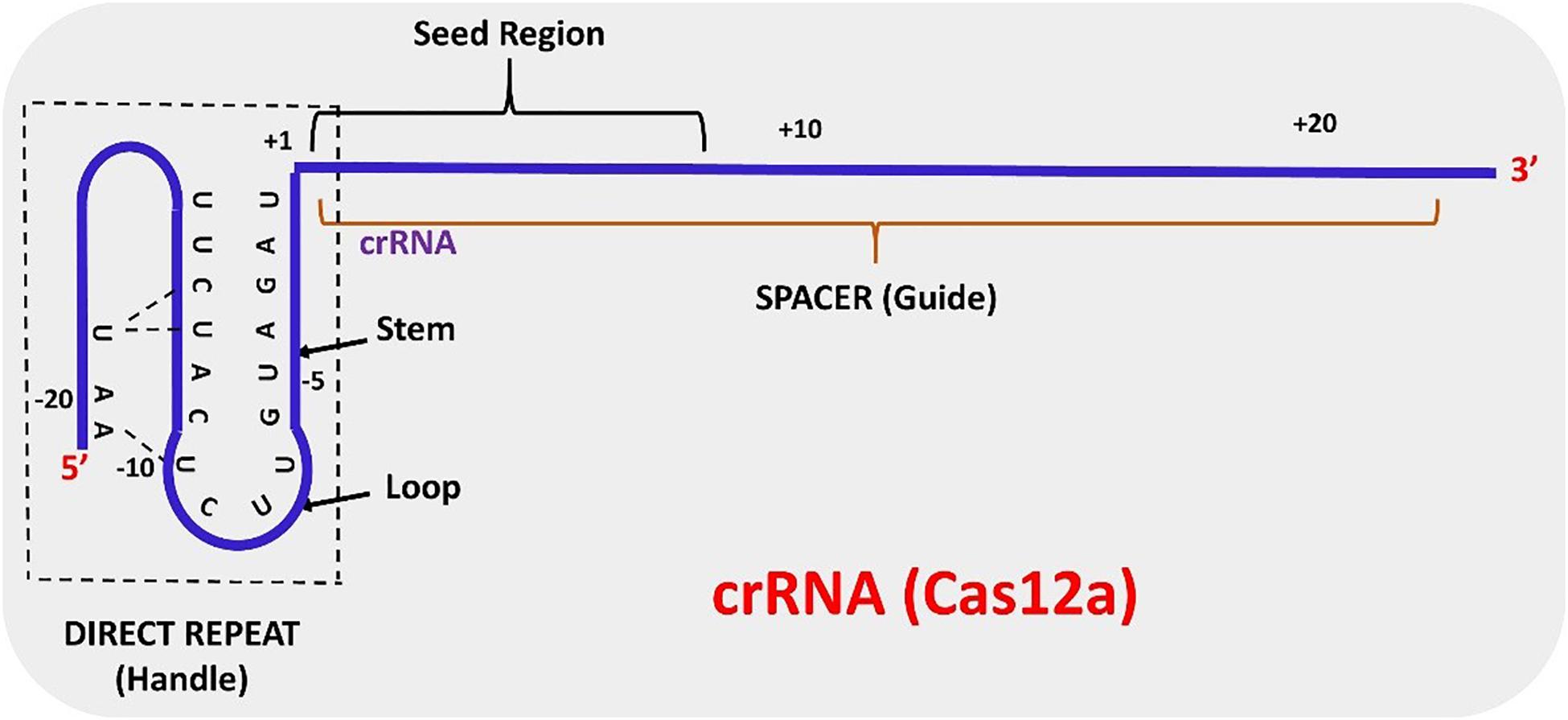



Frontiers Crispr Cas12a Cpf1 A Versatile Tool In The Plant Genome Editing Tool Box For Agricultural Advancement Plant Science



1



Plant Crispr Database
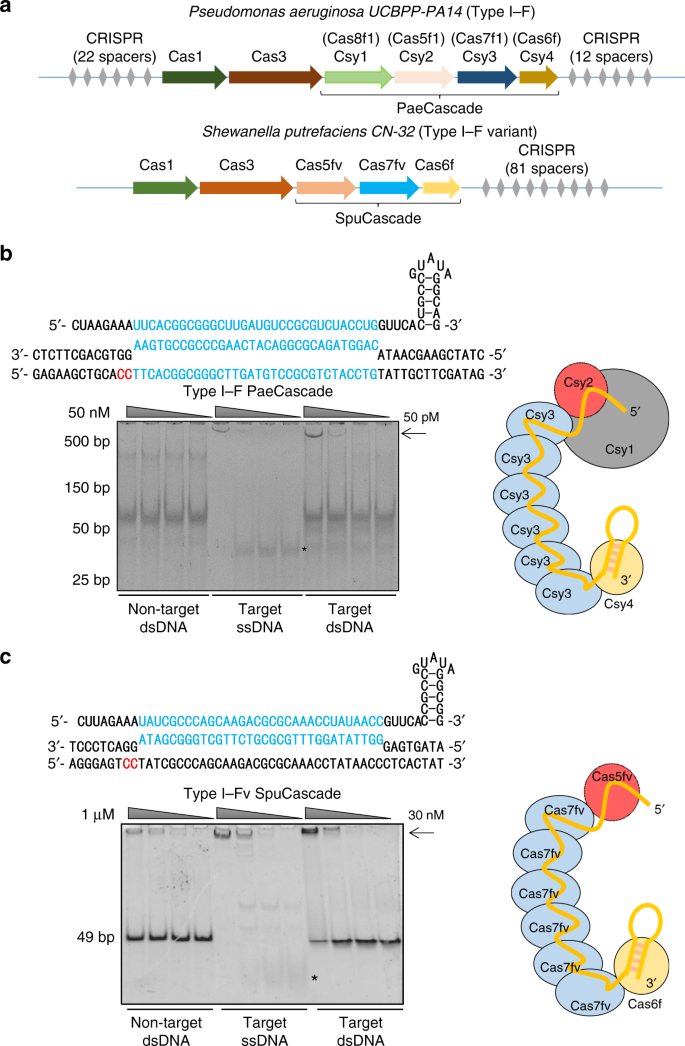



Repurposing Type I F Crispr Cas System As A Transcriptional Activation Tool In Human Cells Nature Communications




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc



Engineering Virginia Edu
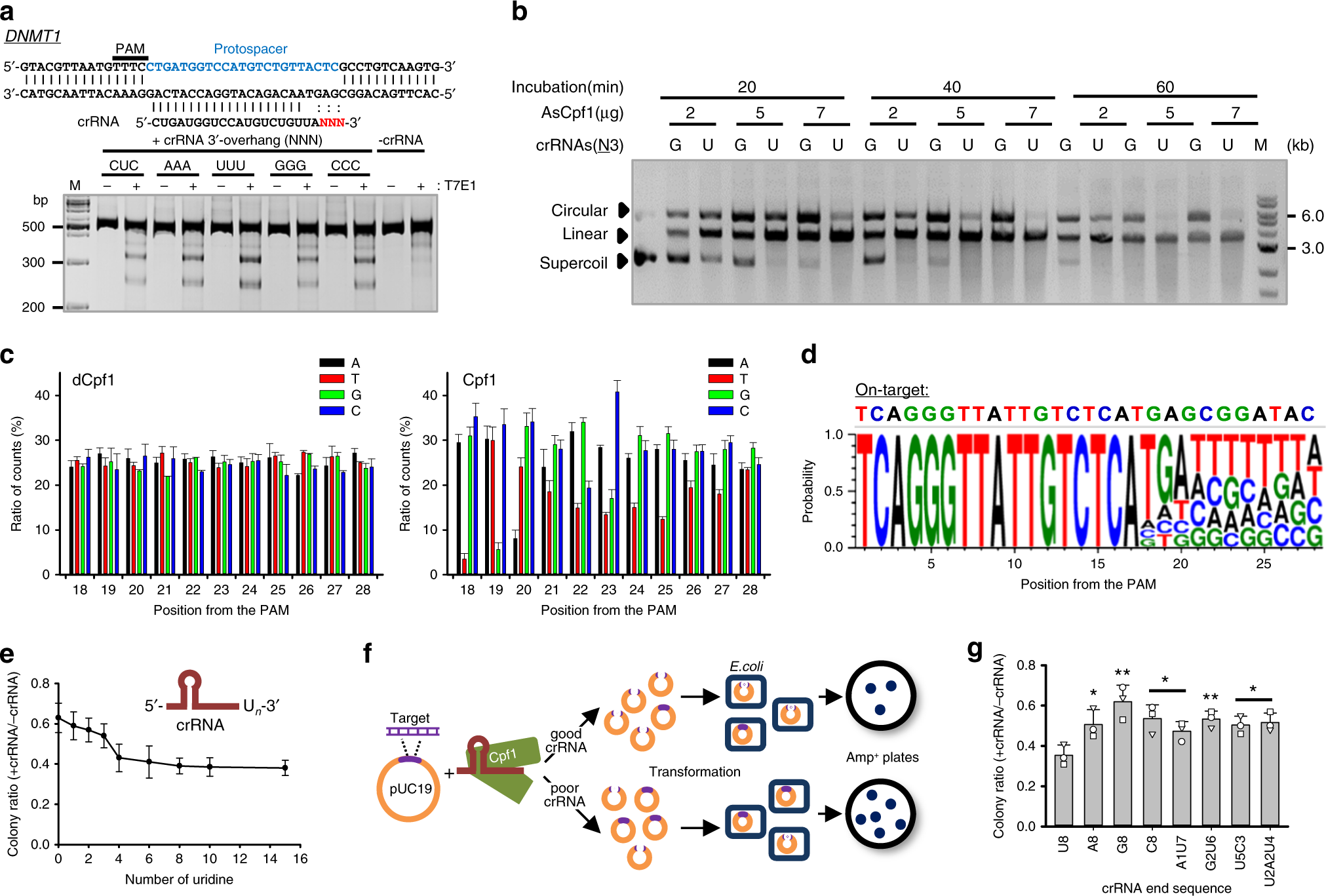



Highly Efficient Genome Editing By Crispr Cpf1 Using Crispr Rna With A Uridinylate Rich 3 Overhang Nature Communications




Genes Free Full Text Spcas9 And Lbcas12a Mediated Dna Editing Produce Different Gene Knockout Outcomes In Zebrafish Embryos Html
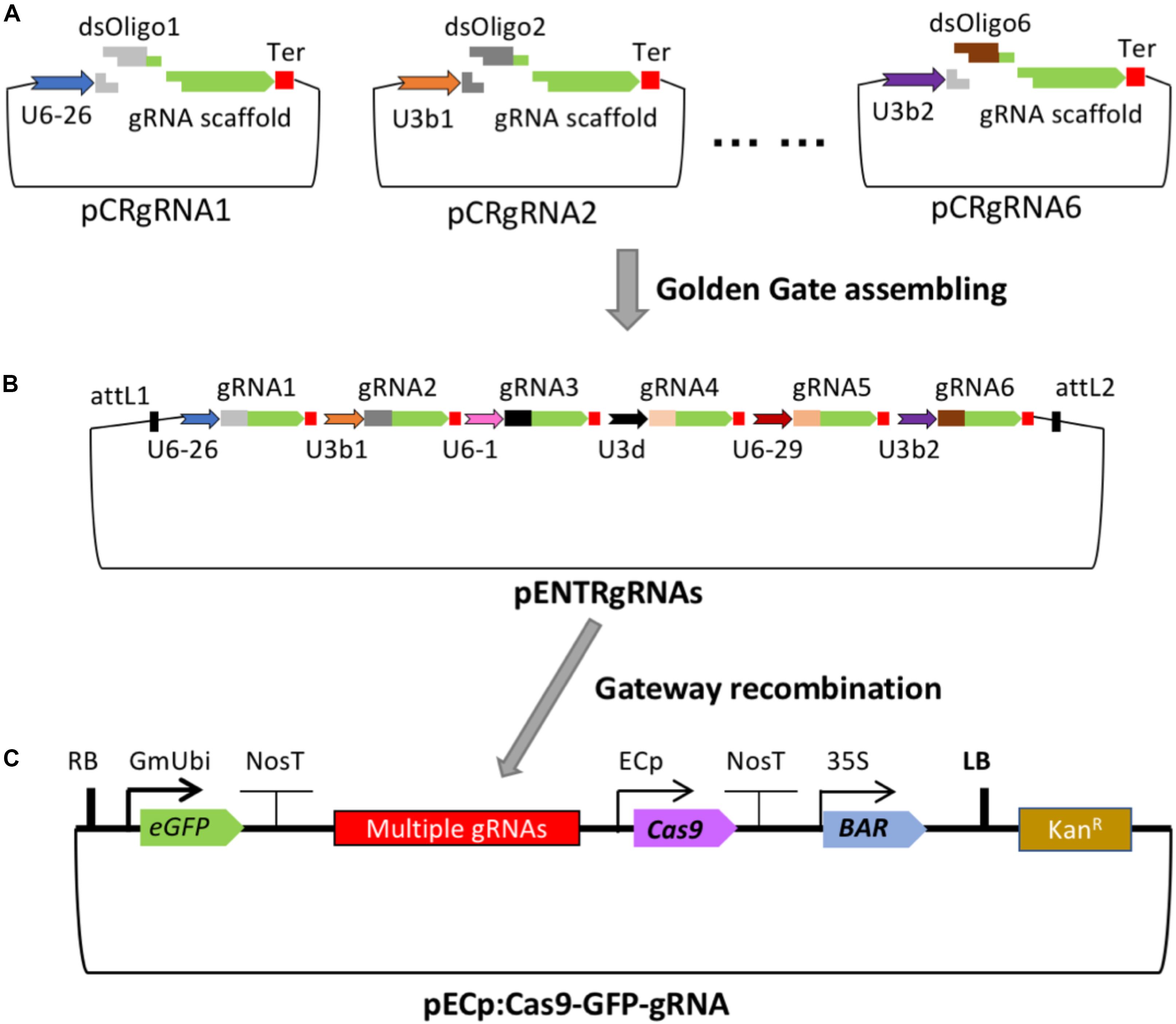



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Based Gene Editing Using Egg Cell Specific Promoters In Arabidopsis And Soybean Plant Science




Genomic Sequences Bound By Cas9 Grna Comprehensive List Of Sequences Download Scientific Diagram




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect




Wu Crispr Characteristics Of Functional Guide Rnas For The Crispr Cas9 System Biorxiv




Improving Crispr Genome Editing By Engineering Guide Rnas Trends In Biotechnology
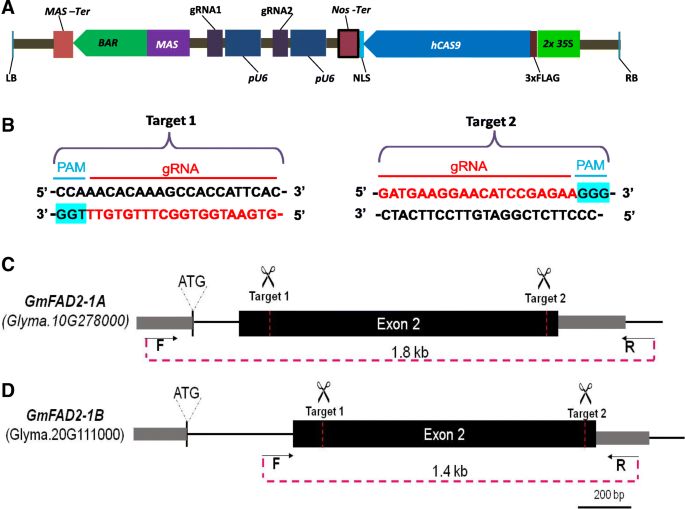



Demonstration Of Highly Efficient Dual Grna Crispr Cas9 Editing Of The Homeologous Gmfad2 1a And Gmfad2 1b Genes To Yield A High Oleic Low Linoleic And A Linolenic Acid Phenotype In Soybean Bmc Plant Biology
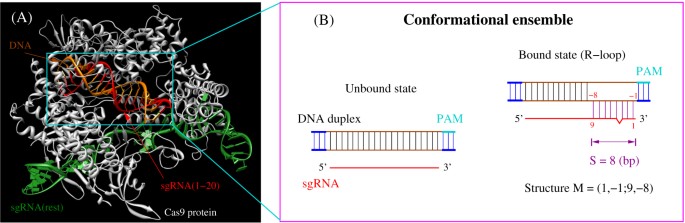



Crispr Cas9 Cleavage Efficiency Correlates Strongly With Target Sgrna Folding Stability From Physical Mechanism To Off Target Assessment Scientific Reports




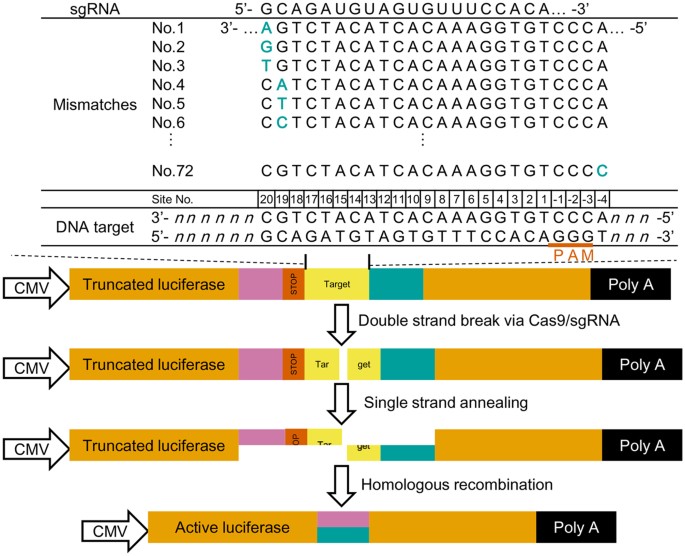
Partial Dna Replacement At The Guide Region Of A Gfp Crrna Induces Gene Download Scientific Diagram




Rule 1 Seed Region A The Relative To Wt Cleavage Probability Of A Download Scientific Diagram
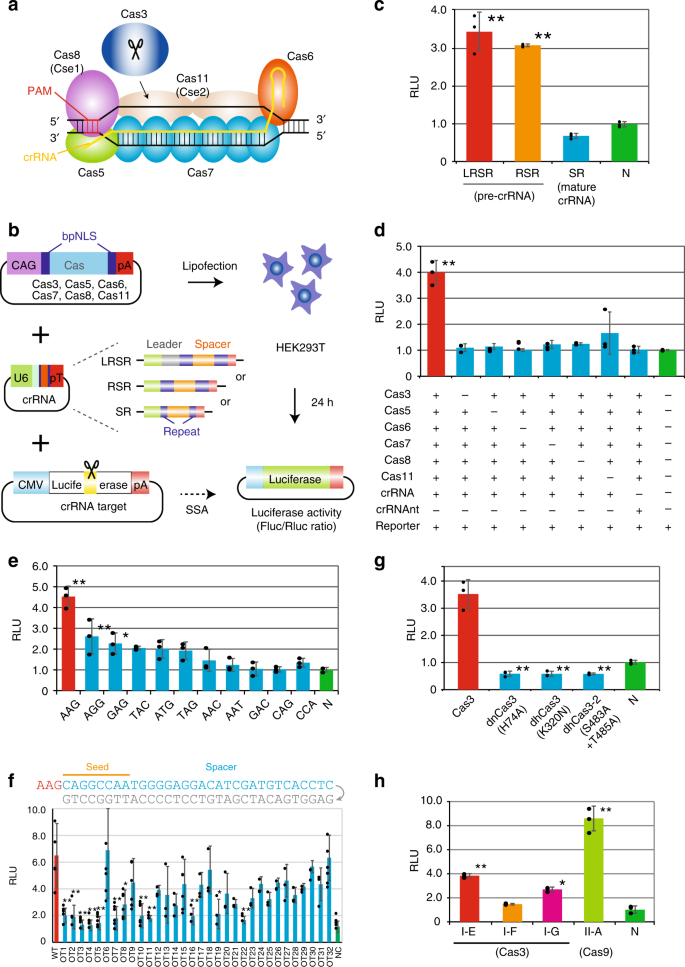



Crispr Cas3 Induces Broad And Unidirectional Genome Editing In Human Cells Nature Communications
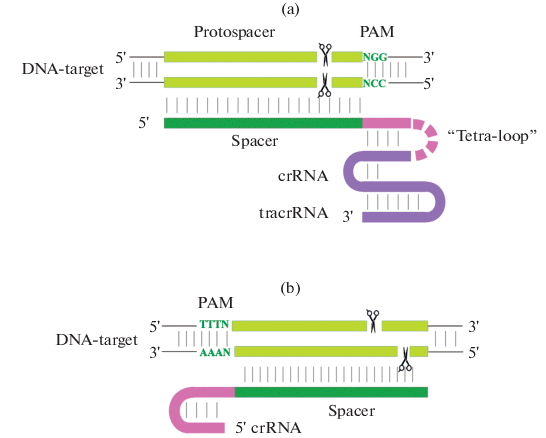



Design Of Guide Rna For Crispr Cas Plant Genome Editing Springerlink



Cell Com
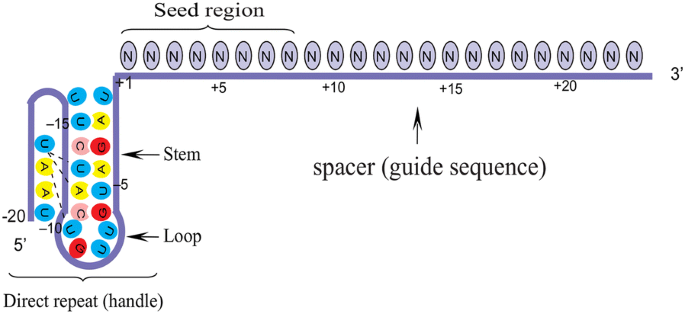



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text
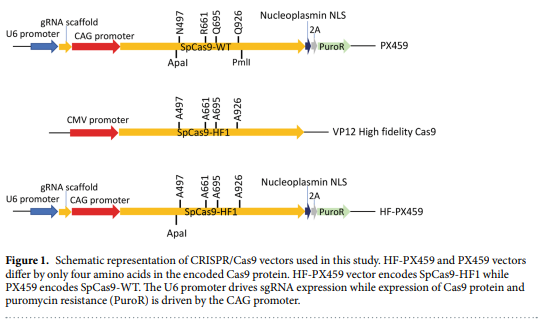



High Fidelity Crispr Cas9 Increases Precise Monoallelic And Biallelic Editing Events In Primordial Germ Cells Engormix



Jove Com




Single Base Resolution Increasing The Specificity Of The Crispr Cas System In Gene Editing Sciencedirect




Crispr Plant
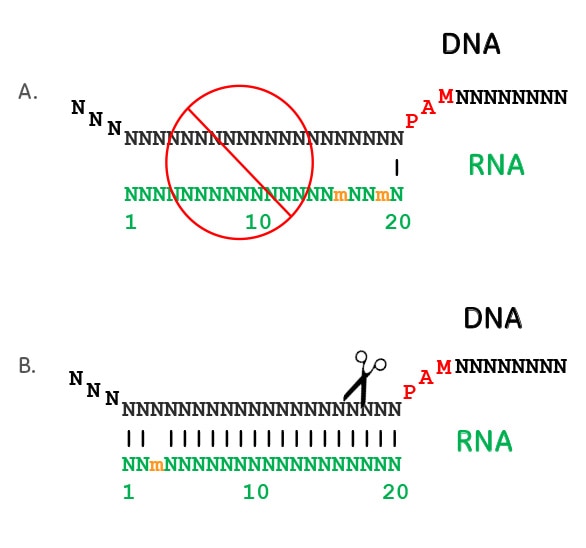



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Specificity




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
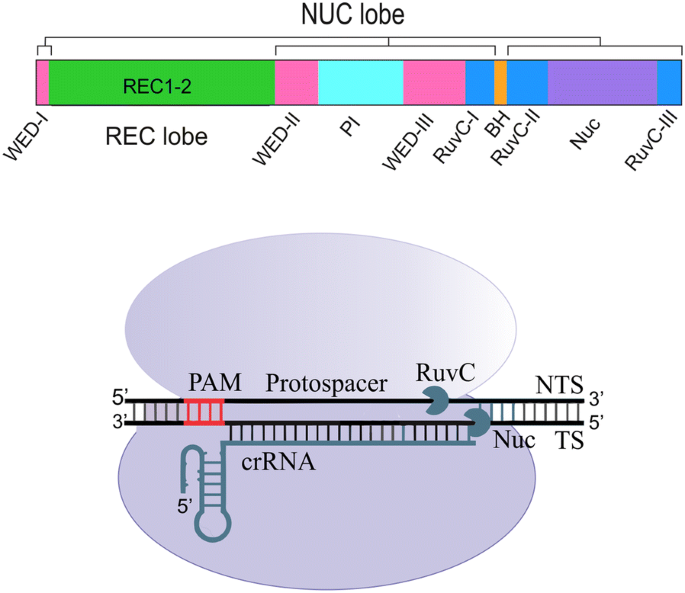



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text




Systematic Analysis Of Crispr Cas9 Mismatch Tolerance Reveals Low Levels Of Off Target Activity Sciencedirect




Schematic Illustration Of Cas9 Grna Genome Editing A Sgrna Mediated Download Scientific Diagram



Frontiers A Crispr Cas9 Based Mutagenesis Protocol For Brachypodium Distachyon And Its Allopolyploid Relative Brachypodium Hybridum Plant Science




Genomic Sequences Bound By Cas9 Grna Comprehensive List Of Sequences Download Scientific Diagram




Enhancement Of Target Specificity Of Crispr Cas12a By Using A Chimeric Dna Rna Guide Biorxiv
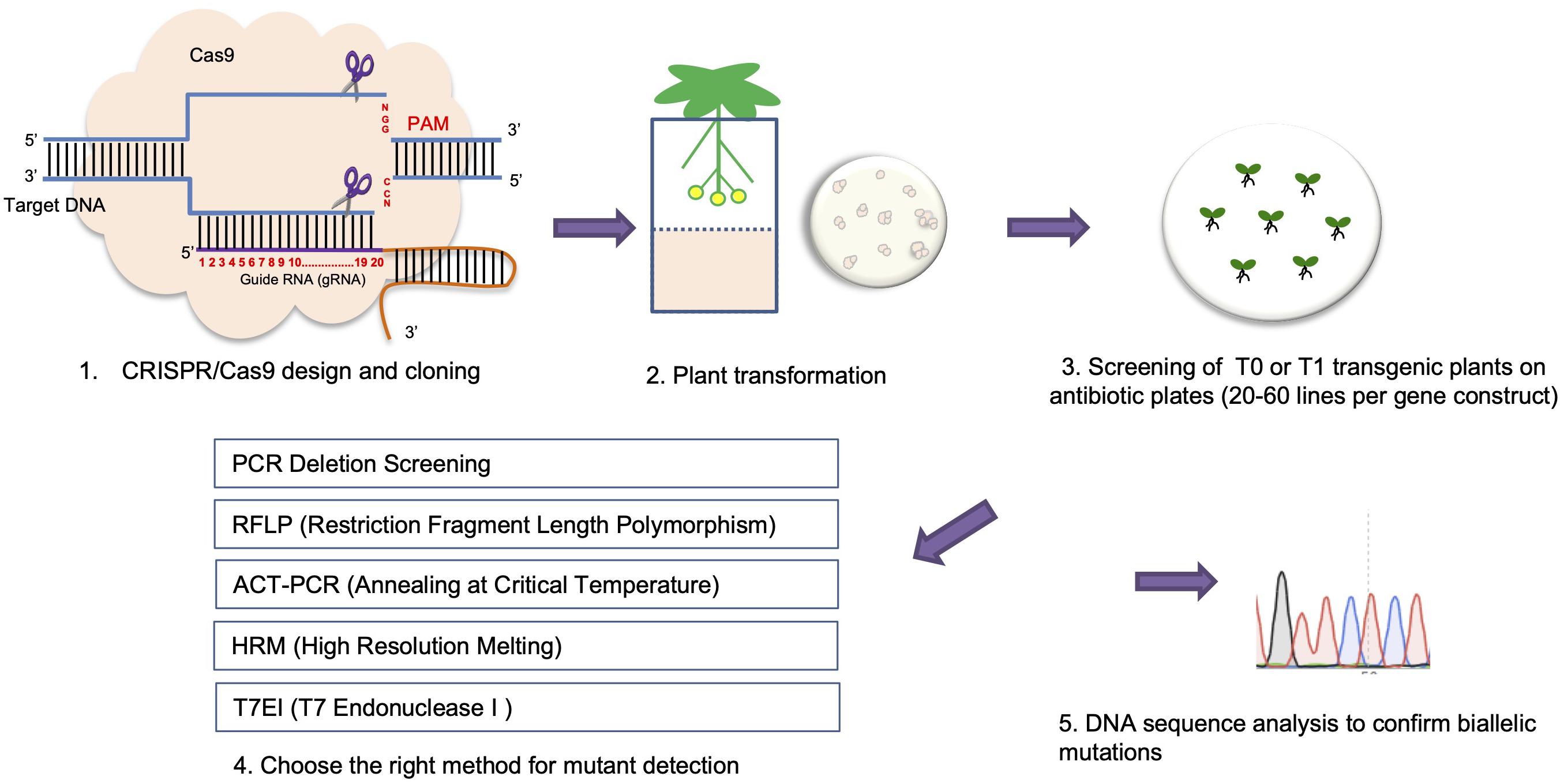



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science




Construct Design For Crispr Cas Based Genome Editing In Plants Trends In Plant Science




High Efficiency Targeting Of Non Coding Sequences Using Crispr Cas9 System In Tilapia G3 Genes Genomes Genetics
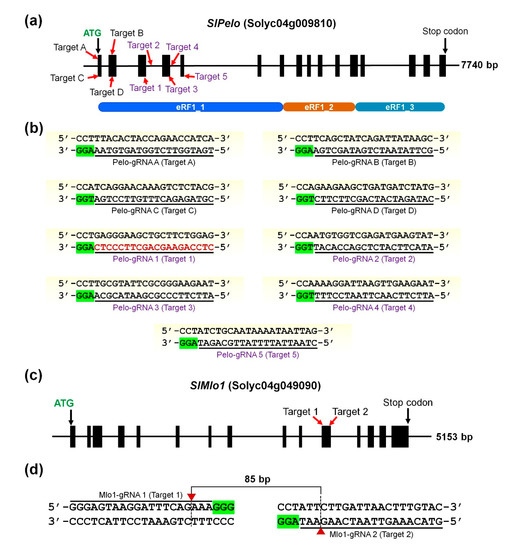



Ijms Free Full Text Crispr Cas9 Mediated Generation Of Pathogen Resistant Tomato Against Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus And Powdery Mildew Html



Journals Asm Org
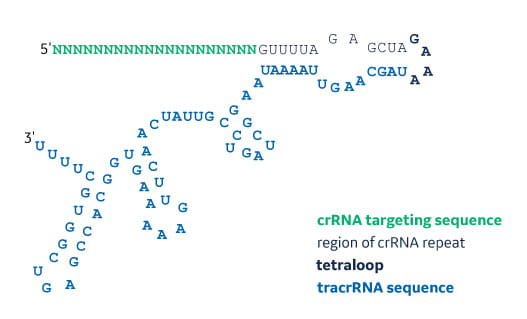



Synthetic Sgrna For Crispr Cas9 Experiments



1



A Cas9 Is Directed To A Specific Genomic Target By The First Nt Of Download Scientific Diagram
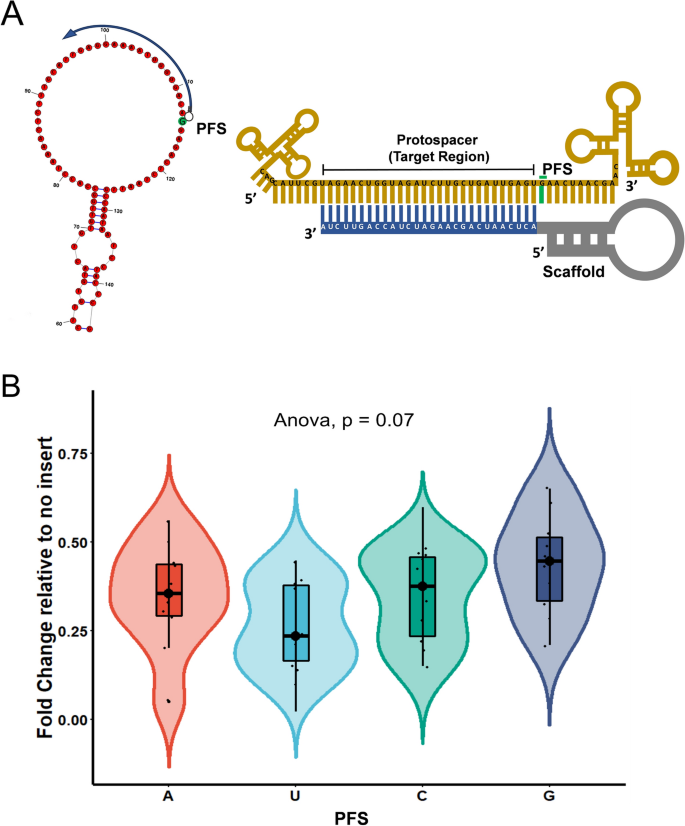



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports
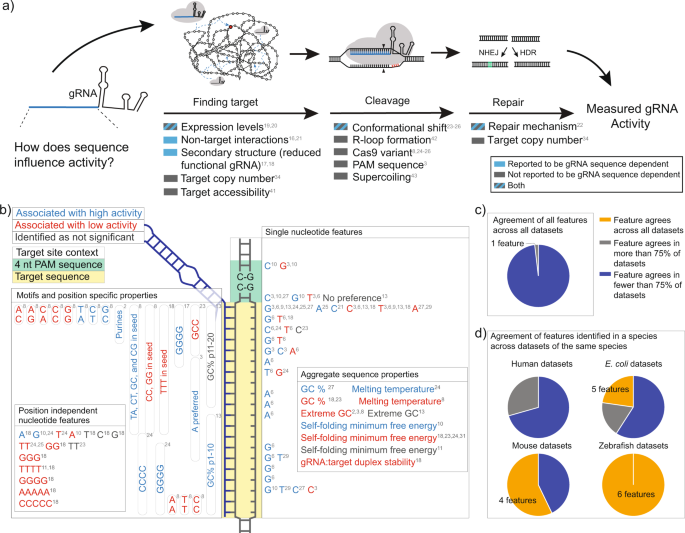



Genome Dependent Cas9 Grna Search Time Underlies Sequence Dependent Grna Activity Nature Communications



View Of A Streamlined Crispr Cas9 Approach For Fast Genome Editing In Toxoplasma Gondii And Besnoitia Besnoiti Journal Of Biological Methods



Cell Com



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports




Crispr Vae A Method For Explaining Crispr Cas12a Predictions And An Efficiency Aware Grna Sequence Generator Biorxiv



1




Systematic Analysis Of Crispr Cas9 Mismatch Tolerance Reveals Low Levels Of Off Target Activity Sciencedirect




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library




Crispr Cas9 Gene Drives In Genetically Variable And Nonrandomly Mating Wild Populations




Boosting Crispr Cas9 Multiplex Editing Capability With The Endogenous Trna Processing System Pnas



Academic Oup Com
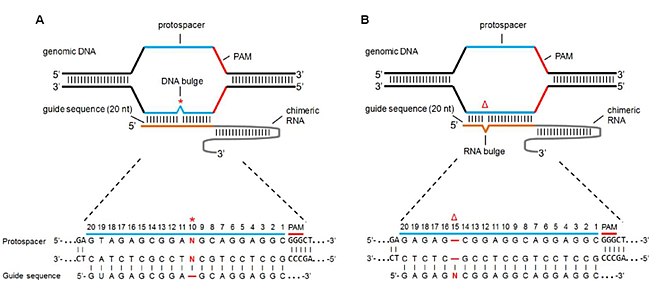



Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia




Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using A Crispr Nuclease System Pnas




Addgene Crispr Guide
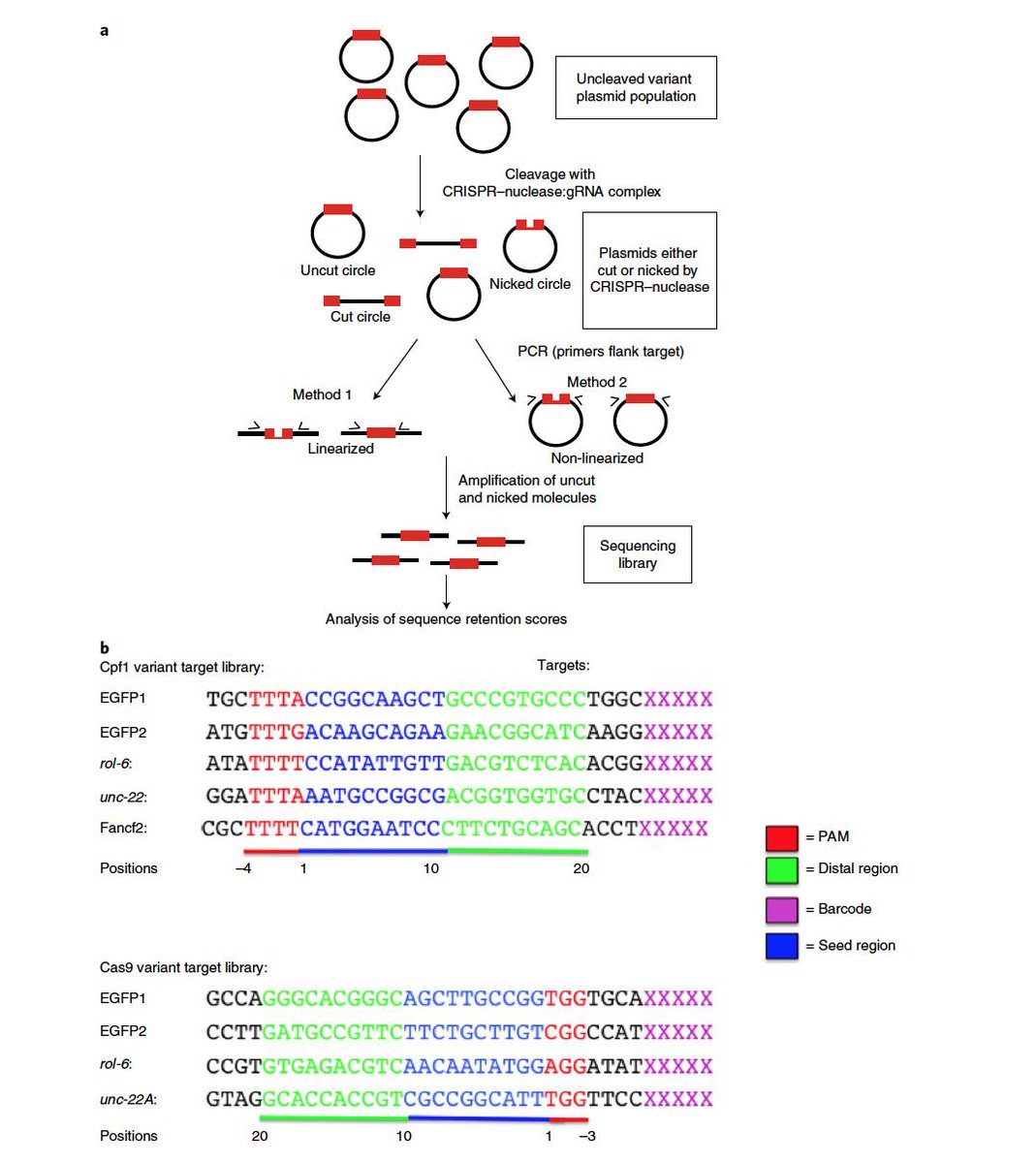



Dr Gaetan Burgio Md Phd Interesting This Paper Published Today In Naturemicrobiol Shows That Crispr Cas9 Or Cas12a Cpf1 Can Display An Inherent Potent Nicking Activity In Yeast This Nicking




Crispr Dt Designing Grnas For The Crispr Cpf1 System With Improved Target Efficiency And Specificity Biorxiv
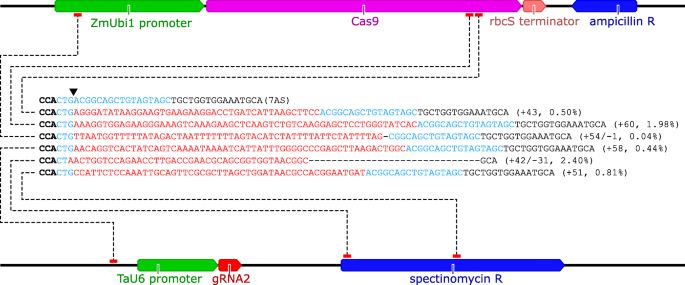



Grna Validation For Wheat Genome Editing With The Crispr Cas9 System Bmc Biotechnology Full Text




Sgrna Sequence Motifs Blocking Efficient Crispr Cas9 Mediated Gene Editing Sciencedirect




Engineered Rna Interacting Crispr Guide Rnas For Genetic Sensing And Diagnostics The Crispr Journal




3 Crispr Cas9 Grna Design Youtube
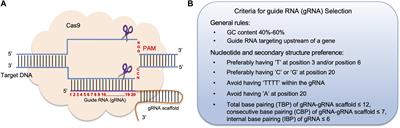



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science




The Complete Guide To Understanding Crispr Sgrna




Get Ready For The Crispr Cas System A Beginner S Guide To The Engineering And Design Of Guide Rnas Ma The Journal Of Gene Medicine Wiley Online Library



Pubs Rsc Org




Setup Of Pmn Fkbp Cas9 And Pmn Grna Constructs A Cartoon Download Scientific Diagram




Addgene Crispr Guide




Crispr Plant




Addgene Crispr Guide




Addgene Crispr Guide
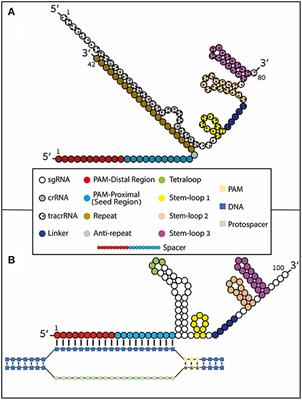



Frontiers Using Synthetically Engineered Guide Rnas To Enhance Crispr Genome Editing Systems In Mammalian Cells Genome Editing



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿